Attracting new customers can be five times more expensive than retaining existing ones, according to a Forbes survey. The rush to increase market share makes organizations throw money at new customers, not realizing that their loyal customers might get disillusioned and leave. The effect is more apparent in B2B circles – retaining and nurturing current clients provides better return on invested time and money. Also, the process of helping current clients can reveal new areas of opportunity that can be beneficial to both parties involved. Such unseen opportunities, or white spaces, are almost everywhere in business interactions, waiting to be seized.
What does WhiteSpace mean in business?
The process of identifying gaps between what is being provided to a customer, and what can be provided to them using other solutions of the provider – is known as the process of white space analysis in businesses. Using sales data, organizations can identify opportunities to cross-sell and upsell, where customers are offered features that improve upon their existing/previous purchase. The process also requires thorough knowledge about the industry, competitors, stakeholders, and the solutions being provided. Insights into emerging industry trends. Executed correctly, white space analysis guides sales teams in identifying ideal customers for their organization, and offers them solutions that are aligned with their goals or issues.
How Does White Space Analysis Work?
The process starts with identifying gaps and highlighting potential areas that can be addressed, and is known as white space mapping. There are two types based on the way the mapping is focused on – internal and external.
Internally focused mapping identifies the strengths of the organization’s solutions/products, and lists the strengths, opportunities, and areas of concern. Internal mapping helps highlight market barriers, and teams can work towards addressing the obstruction by offering new solutions, modifying existing ones, or targeting a different section altogether.
Externally focused mapping lists the products or services that are succeeding in the market, analyses the ones that are failing, and identifies where potential gaps are.
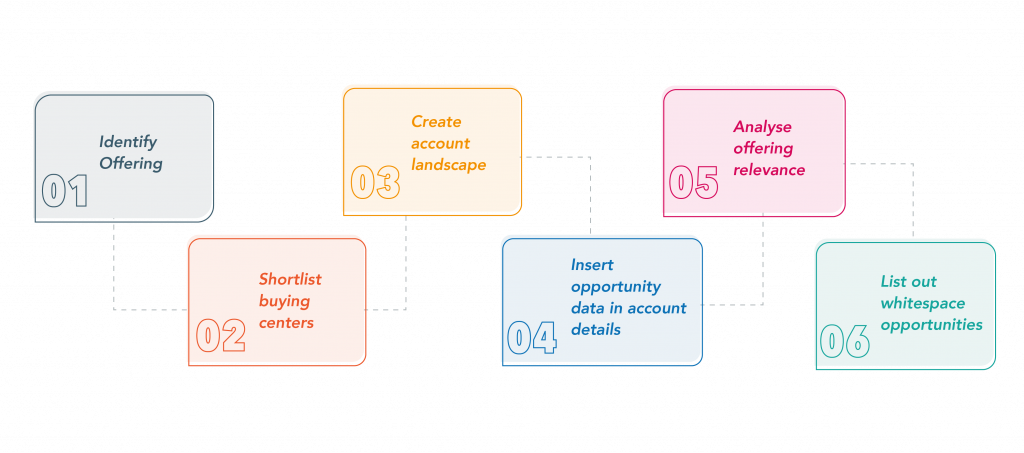
Key areas of focus during whitespace analysis
Whitespace analysis is all about looking for value where others think none exists, and it can happen only if sales team members are actively sharing and updating the information they have about customers. This differs from the typical account management process, which can be represented as below:
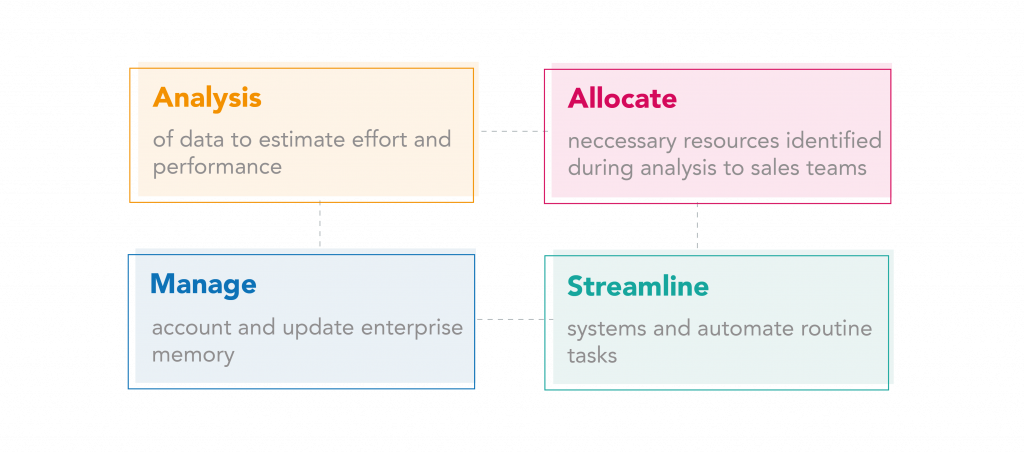
This institutional know-how, with the help of key account management software, can be structured into an enterprise memory that can be used by any and every member of the team and take up from the last interaction. The process requires teams to consciously focus on the customer and the business, and here are a few pointers for the same:
1. Arranging and understanding current data
Previous purchases of customers is a good place to start, as it provides details on the services that customers need. Details like opportunity type, industry, account type, products used – can provide information about a customer’s state, and the details can be used to highlight pain points and how products from vendor organizations can solve them. For existing customers, the incremental charge they may incur to use the new feature/product should be clearly communicated.
2. Limiting market scope
Sales executives joke about ‘anyone and everyone’ being their target audience; while this helps teams reach a wider variety of users, there are few products and services that are universal. Customers who end up disappointed because of wishful marketing can lead to bad word of mouth and lower sales. Clearly defining the target, therefore, holds a lot of importance. Identifying customer challenges, gaps between product and customer workflows, what consumes the customer executive’s time, and many other factors direct the retargeting efforts.
3. Keeping an eye on what competitors are doing
A common misconception is to think of white space as an area where no competitors are present. This is never the case. There are several competitors almost always, and analysing their marketing tactics can reveal their strengths and weaknesses. Comparison to the expected customer profile/solution to their organizations, gives sales team members a way to identify the gaps in their solution.
4. Treating current customers the same
Sometimes when vendor organizations try to pitch for a substantial business, their existing clients might run into issues that need immediate attention. Learning and understanding their needs can also reveal potential white space opportunities. By asking the customers about improving their everyday workflow, sales teams can shortlist features and ideas that can improve overall experience. Opportunities for optimization, tweaks, or adding new features exist even in the most efficient companies. Being proactive assures customers that vendor teams are on the job all the time, and being receptive to feedback and responding quickly with a detailed response drastically increases the chances of them renewing their contracts.
5. Treating all new opportunities the same
Since white space refers to the untapped areas of engagement with current customers, chances are teams ‘taking it easy’ are high. After all, they know the customers, or at least most of what is there to know. But after finding the right target and product, the next step is to leverage the data – no matter how well-acquainted the customer is. In fact, the pre-existing relationship can speed up matters, when sales team members directly reach out to the potential customer and set up a meeting. Other avenues, like retargeting them via marketing efforts or creating a product, service, or feature to address their problems can also take the relationship forward.
Benefits of White Space Analysis
Whitespace analysis leads to a better understanding of the buyer. Identifying the target market becomes easier, their pain points become apparent, and the overall customer buying journey can be analyzed. The knowledge gained from whitespace analysis can guide sales teams to customize their sales pitch to address specific customer needs. Identifying new customers and segments paves way for the expansion of the offering into newer markets. Increased customer insights can help decide the target, the value props that should be highlighted, if the solution for the white space is viable, the effort and costs needed to expand into identified gaps, and a lot of other important factors.
The analysis process also informs the approach that sales teams should take. Personal preferences of customer organization executives should lead the presentation, as it is essential for them to take in as much information as possible. Some people are more receptive to visual presentations, some might prefer numbers, and some might just want to go through the document without having anyone to speak to them. There is no ‘one approach’ that works better than others – except understanding that it is different every time. Sales teams can take call based on the information available to them, and settle on a soft sell or a hard sell methodology. The sales strategy gets attention in whitespace analysis too – and areas that require the focus or withdrawal are highlighted. The data provided by whitespace analysis act as guardrails for the sales process, and streamlines innovative thinking.
What are the exact steps of the whitespace analysis?
The process of white space analysis can be done manually, but the right tool can ease the matter a lot by gathering and analysing the customer data, based on the parameters set. The process involves following steps:
1. Market assessment
To understand the competition in reference to the market it operates in, sales teams can start with reception figures. Reviews, updates, news – everything helps in determining the next action of competitors. If they’re launching new products or services, comparing it with the company’s solution can shed light on the way the market is going. Examining the audiences targeted by the competitors (if they’re existing customers or is this a new market push), the needs they’re trying to fulfil for these audiences, and how the reactions are to the changes.
New entrants in the market, even though they have relatively insignificant market share, can be banking on a disruptive feature. In software-related industries the majority of innovation comes from smaller, newer entrants and other organizations can adopt similar innovations if needed. While chronicling upstarts, sales teams need to understand how the status quo is being challenged, are there any new methods to meet consumer needs, are they establishing a new category, and consumer reactions to the services.
Staying up to date on trends and societal shifts speed up the responses that organizations can have for changing customer demands. Sales team members can follow leading bloggers, influencers, and research organizations to know what is happening and changing, and keep the rest of the organization updated on the same through enterprise memory.
2. Customer assessment
Talking to consumers through various channels gives a clear picture of what they like, what they need, and what their problems with the current options are. By approaching customers’ problems with a human-centred design mindset, sales team members can immerse themselves in consumers’ lives and uncover needs that can be met. Observing the workarounds that employees use, their body language and habits, how their environments, surroundings, and social cues impact their actions, and empathizing with them clarifies their motivations and emotions to everyone involved. Deep understanding of a customer’s lifestyle and experience leads to a deep understanding of their issues, and identifies changes that can deliver new benefits in addition to the solution. Taking care of known customer needs dictates the direction of approach too, as the best way to solve issues might change as time and situations do.
3. Determine white space by layering both
A clear understanding of consumer needs and the competition allows team members of vender organization to map requisite deliveries to the competitive features. The data shows the needs that are completely met, the ones that are not, and finally – the ones completely ignored. The blind spot might be on the competitor side as well as the organization looking for solutions – sometimes the simplest of solutions can be overlooked because of the workload. Cross-referencing such needs and market trends together provides a fair idea of the time and effort required.
4. Choose options that fit with the product vision
Size of enterprise accounts can launch medium-sized vendors in the big leagues, and the size of contracts can tempt teams to pitch solutions that may not be entirely up their alley. The list of opportunities thrown up by whitespace analysis should be evaluated against brand values or what the product aims to achieve. By considering the alignment with the brand equity, sales teams can rate identified opportunities. Factors like the amount of extra effort required to understand the need (before commencing the development of the solution), if the customer perception of the product or organization is different from the opportunity area, and the unique positioning and selling points of the product that answer customer issue, determine what steps can be taken to match the needs.
The choices available in front of the sales teams can be endless, and succeeding with one doesn’t mean that there aren’t other opportunities in the same white space.

Sell smart and fast
There is no end to the sales process – once team members understand how they can make a difference by highlighting hard to grasp issues and position the product as an ingenious way of handling it, they grow with the solution they sell. They can stay up-to-date with the market trends and customer needs with whitespace analysis, and identify growth opportunities that measurably improve the bottom line.
One of the most effective ways to use whitespace analysis is to utilize it to identify cross-selling and up-selling opportunities by digging through sales data. Cross-selling is the process of satisfying the additional needs of customers that the primary product is unable to fulfill. Up-selling is where the end goal is to increase the cart value not by introducing new items but by increasing the size or quantity of the initial purchase decision. White Space Mapping provides deep insights into customer behaviors and buying trends. A quantitative approach gives you a tangible framework to identify gaps between products and services that your customers have already bought from you and the ones that you can sell to them.
Effective whitespace analysis leads to higher rates of up/cross-selling using the right tool. Learn the best practices of cross-selling and upselling , all executed within your CRM and identify unexplored opportunities for the growth of your business as well as your clients’ business in 2022.
 On-Demand Webinar: Unfiltered take on AI in Account Planning: Meet DemandFarm’s KAM AI
On-Demand Webinar: Unfiltered take on AI in Account Planning: Meet DemandFarm’s KAM AI 


